Inflammation of the navel in chicks

2023-08-30 14:18:32
Omphalitis is a non-infectious condition that appears in chicks and is characterized by the fact that the navel remains open, inflamed and does not heal
Causes:
1 / lack of attention to the cleanliness of the hatching eggs and lack of interest in evaporating it with formalin, resulting in severe bacterial contamination .
2 / contamination of the shell with some bacteria that seep into the eggs through their pores .
3 / some mothers producing hatching eggs were infected with some bacteria that are transmitted to the hatched eggs and to the fetus through the umbilical cord .
Some infections occur and the navel fails to heal and remains open, which gives the opportunity for some opportunistic bacteria and leads to its inflammation and swelling .
4 / the presence of stress factor stress factors such as high heat or excessive cold, or leaving it in the hatchery for too long before transferring it to the farm, or delaying the provision of food and water, lack of vitamins, mineral salts and necessary antibiotics .
Symptoms:
1 / this condition appears in the first ten days from hatching .
2 / infected chicks tend to huddle under heat sources and show signs of general weakness .
3 / inflammation appears in the navel area and in severe cases the navel opening remains wet and in mild cases the navel is
Dry .
4 / the abdomen swells and some gases may form with an unpleasant odor .
5 / cases associated with omphalitis may appear such as blockage of the pool opening and may lead to the death of infected chicks .
6 / the duration of the disease is a week and the death rate varies between 10% -30% and it is not possible to treat any chicks that have taken the infection .
Anatomy p. m
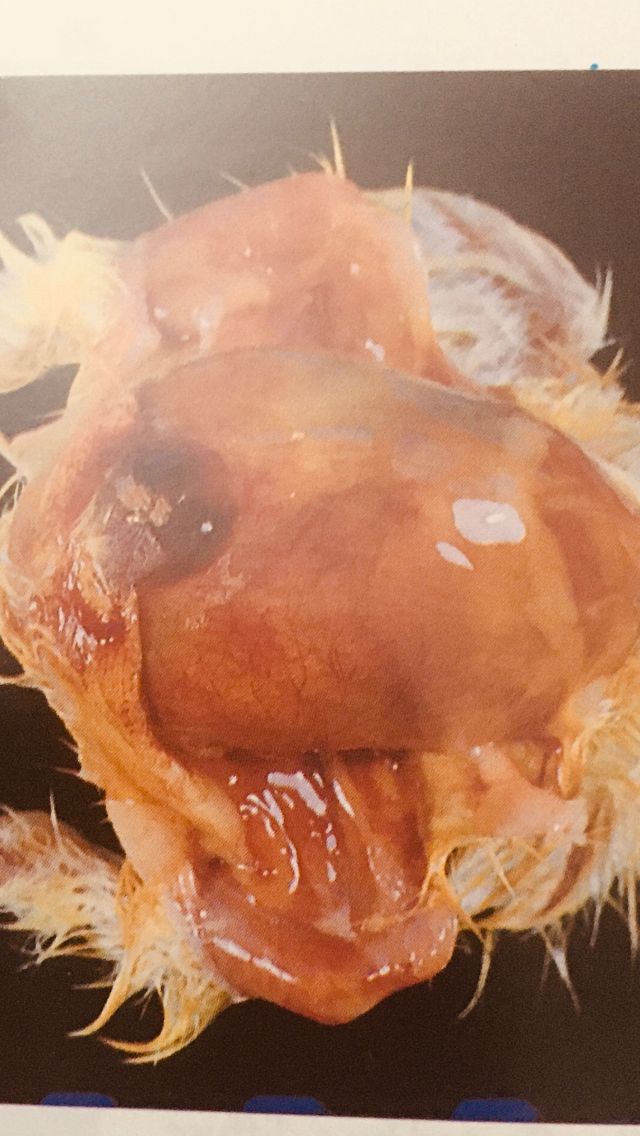
1 / non-absorption of the yolk sac, whose walls are inflamed and its size swells, and its contents become liquid, viscous and smelly
2 / inflammation or Demy in the muscles of the chest and abdomen
3 / in some cases you may see peritonitis peritonitis .
4 / in some cases, the yolk sac may burst its contents inside the abdominal cavity abdominal cavity .
Prevention and treatment:
1 / there is no treatment for infected chicks .
2 / can help regulate the temperature of the incubation area .
3 / complete disinfection procedures must be observed in the hatching laboratories, where only clean, unopened and evaporated eggs are hatched before hatching
Also egg dishes and Hatcher drawers should be thoroughly disinfected and hatching hatched before and after laying eggs as well as after hatching and the steaming process should extend to an hour as well as after hatching and the steaming process should extend to at least an hour and formalin and potassium permanganate should be at the rate of 40 cm formalin + 20 g potassium permanganate per cubic meter of hatching volume .
4 / provide a therapeutic package containing a suitable antibiotic such as tiramycin or chlortetracycline and an increase in vitamins for 14 days .
5 / in drinking water, one of the antibiotics such as ( tiramycin-neomycin-arthrocin) is introduced ......Etc.)
At the rate of 10 g/ chick for 5-7 days .
6 / vitamin AD3E is introduced into drinking water at the rate of 3000-5000 units / chick for 5-7 days .
الموضوعات المشابهه

The use of dietary nucleotides in poultry

Manufacturing a domestic product that competes with

Body language in chickens

Diseases (infectious Bursa diseases)
Coccidiosis in poultry production

26 cattle and 1400 chickens died in

Contract agriculture and its relationship to sustainable

Some common diseases in poultry

Tips for broiler breeders to deal with

A series of animal diseases

The role of nanoparticles in animal and

What's after spawning.?

Comments
Add comment